Different image file formats explained, including DNG, JPEG, TIFF, PSD and RAW
What are the different file formats, and what does each format mean?
DNG
Adobe’s own Raw format, which a number of cameras use for their own default Raw files. You can convert Raw files to DNG using the Adobe DNG Raw converter, and as the company has pledged to continue supporting the format, this would effectively make them futureproof.
JPEG
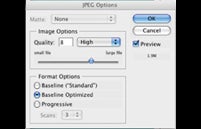
The most common format for storing images from a camera. Files are typically compressed, meaning that they take up less memory but at the expense of data.
TIFF
TIFF files are only produced by a select number of cameras due to their size and drain on processing, but they may be saved uncompressed which is great for retaining maximum detail.
PSD
A format used by Adobe Photoshop in which to store files. The format is flexible in that it supports transparencies, colour spaces and other elements that may be altered later on.
RAW
The universal name for unprocessed images created by DSLRs, which allow you to set your own processing later on.